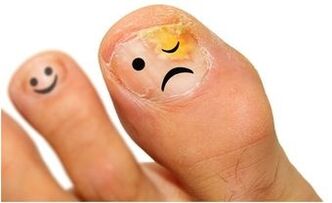
Epidermophytosis of the feet is a class of fungal diseases characterized by damage to the feet, interdigital areas, and nails. It has a high prevalence, usually observed in people over 30 years of age (rarely in children), prone to chronic disease with alternating exacerbations and remissions.
Mycoses are infectious diseases caused by pathogenic or opportunistic fungi. Mushrooms are lower plants that do not have chlorophyll, and ready-made organic substances are necessary for their vital activity - they get them by settling on the skin of people and animals.
The causative agents of fungal infections are very persistent, which distinguishes them from other microorganisms. Fungal diseases of the skin are the most common worldwide. Human contact with fungi is constant - at home, at work, in offices, in nature, in swimming pools, saunas and so on.
Where can you get mushrooms?
You can get infected with a fungus in many public places - baths, saunas, beaches, gyms (especially in showers), when wearing someone else's shoes.
The risk of infection increases many times if a person does not maintain their hygiene.
symptoms of the fungus
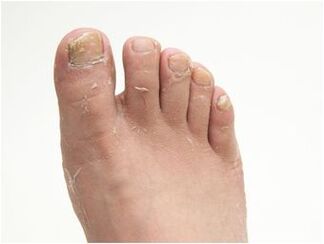
The course and development of the disease are influenced by the physiological properties of the skin of the feet, increased sweating, disorders of the endocrine system, leg injuries. The causative agents of the fungus can be in a "dormant" state for a long time without revealing themselves as symptoms. If they are disturbed in the body, they can be activated. Epidermophytosis of the feet is characterized by the presence of several forms of the disease, which can be supplemented by damage to the nail plates.
You can note the defeat of the fungus in the presence of several symptoms:
- the nail plate changes its natural color: yellow or dark color is usually fixed, but the nails can even turn white or completely black;
- Tissue keratosis under the plate: outwardly it looks like a hard growth has appeared under the nail;
- thickening and delamination of the plate;
- Deformation of the nail: its protrusion, lateral growth, ingrowth into the skin;
- Fragility of the nail plate: chipping of its part is possible.
As the disease progresses
The first manifestations of the disease begin in the spaces between the fingers, especially between 4 and 5, since between them there is the smallest distance. A slight itching sets in and over time a strip of thickened and slightly scaly cuticle appears at the finger crease.
After 2-3 days, a small crack is already formed, from which a serous fluid is released, which serves as an excellent medium for the successful reproduction of the fungus. The hard layer of epidermis may fall off, revealing a dark pink area underneath. The progression of the disease leads to spread to all fingers and the adjacent side of the foot.
The fungus can penetrate through damaged areas of the upper skin into the deeper layers behind the epidermis. The disease is accompanied by an eczematous reaction. Fluid-filled blisters form on the skin, which are very itchy. Over time, they can coalesce and erode, resulting in the appearance of weeping areas.
Relation! When examining the skin affected by the fungus, it was found that the "bare" wet surface appearing under the vesicles does not contain the pathogens themselves, but is only a consequence of their activity.
Without timely treatment, the fungus affects the entire surface of the foot and fingers, sometimes reaching the area above the heel. There is an instability of the course - the disease then slows down, and then again intensifies.
Without treatment, the disease can drag on for many years. At the same time, with pathogenic streptococci there is a high risk of complications: the fluid in the vesicles begins to fester, the foci of inflammation spread beyond the original limits, the foot swells badly. Due to pain in the legs, it becomes difficult for a person to move. In addition, there may be complications in the form of problems with the lymph nodes.
The development of epidermophytosis usually occurs in the summer months. At this time, sweating increases, fingers often get wet, and increased moisture in the interdigital areas creates favorable conditions for the introduction of the fungus and its active reproduction.
Mycosis usually manifests itself on 1 and 5 fingers, spreading from the free side. The nail gradually thickens, acquires a yellowish tint and an uneven sharp edge. Over time, pronounced subungual hyperkeratosis of varying degrees is manifested.
treatment of athlete's foot
For successful therapy, much attention must be paid to the treatment of lesions.
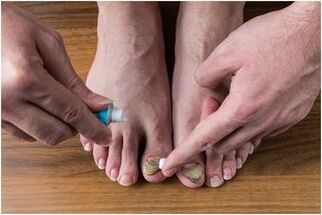
A fungus sufferer should take a foot bath with potassium permanganate daily. It is necessary to remove the crusts, pierce the bubbles and remove the "rim" along the borders of the erosive areas and the suppurating bubbles.
After the bath, it is necessary to apply medical bandages to the affected areas soaked in an aqueous solution of copper sulfate (0. 1%) and zinc (0. 4%) or a 1% solution of resorcinol. After the weeping spots have started to heal, fungicidal alcohol solutions are used. If necessary, the set is supplemented with fungicidal ointments.
Achieving the desired result does not depend on the drugs used, but on the correct order of their application according to the current situation in inflammatory processes.
A large role is played by additional treatment after the completion of the fight against lesions, as it helps to prevent recurrence. The skin of the feet is wiped with 2% salicylic alcohol or 1% thymol, and the use of 10% boron powder is also required. To eliminate and prevent the appearance of fungus in shoes, you need to wipe them from the inside with a solution of formaldehyde, wrap them in a dense cloth for a couple of days, and then dry them in the open air. With socks, tights and stockings, everything is simpler - they only need to be boiled in this solution for 10 minutes.
If there is a complication of pyococci, antibiotics are used. Be sure to keep bed rest.
prevention
To prevent the occurrence of fungal infections, the following preventive measures should be taken:
- Owners of swimming pools, gyms and baths should pay more attention to disinfection - conduct thorough treatment of the premises according to the established schedule.
- If a fungal infection is suspected, you should immediately consult a doctor to immediately stop the disease.
- Before going to bed, it is advisable to wash your feet with soap and cold water and dry them thoroughly until dry.
- Don't use someone else's shoes;
- change socks or stockings daily;
- When visiting swimming pools, baths, showers in gyms, you should have your own shoes.